It’s fascinating to think about how our quest for connection has evolved over time. From the humble beginnings of Match.com in 1995 to the swipe culture introduced by Tinder, each step in the evolution of dating apps mirrors our changing societal norms and technological advancements. This journey is crucial for anyone wanting to understand how these platforms can serve us now and in the future.
As we dig into this history, we’ll also uncover insights from detailed research on user behavior and technological innovations. These insights not only reveal where we’ve been but also guide what’s next. To fully grasp how these shifts affect us personally, it’s helpful to map out significant milestones that marked each advancement in online dating.
The evolution of dating apps encompasses key milestones from the launch of Match.com in 1995 to the introduction of swipe-based features by Tinder in 2012, reflecting shifting technologies and user preferences. This progression highlights how dating platforms have increasingly focused on compatibility, inclusivity, and innovative interaction methods, adapting to cultural changes and user demands over the years.
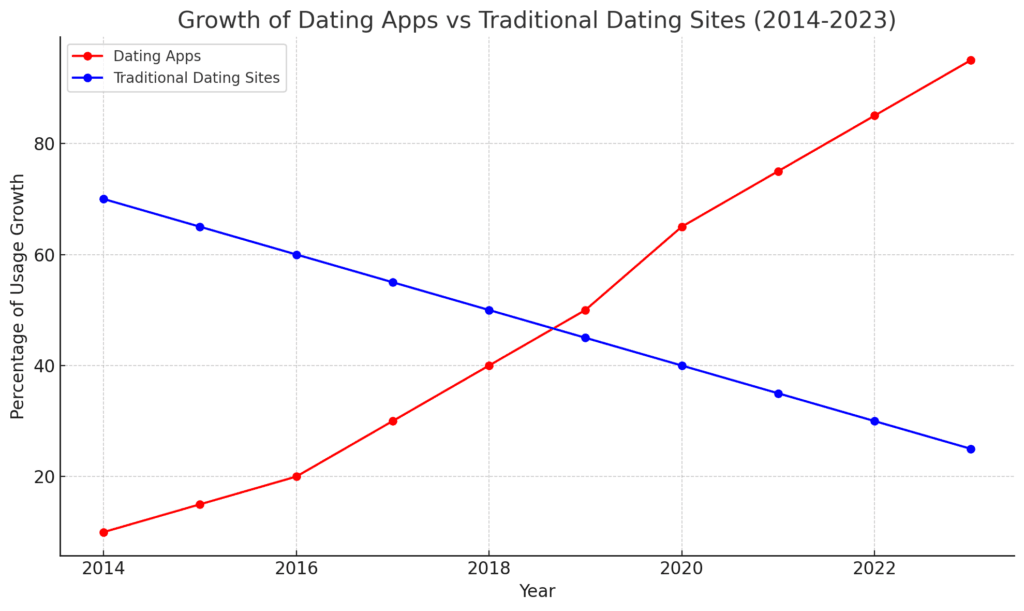
Earliest Evolution of Dating Apps
Key Milestones
- 1995 – Match.com launches, pioneering online matchmaking.
- 2000 – eHarmony starts, focusing on algorithm-based compatibility.
- 2003 – Plenty of Fish launches, offering a free alternative to paid dating sites.
- 2004 – OkCupid was launched, and personality quizzes were used to connect people.
- 2007 – Zoosk debuts, integrating dating features with social media networks.
- 2009 – Grindr launches, the first major location-based dating app for the LGBTQ+ community.
- 2010 – Badoo expands its social discovery network, quickly gaining popularity in Europe and Latin America.
- 2012 – Tinder launched the “swipe” feature, which makes dating app usage more engaging and mobile-friendly.
- 2014 – Hinge relaunches, moving away from swiping towards more serious, connection-focused dating.
- 2014 – Coffee Meets Bagel popularizes curated daily matches to encourage more meaningful connections.
- 2014 – Her launches, focusing on LGBTQ+ women and creating a community-focused dating experience.
- 2015 – Bumble launches, emphasizing female empowerment by allowing only women to make the first move.
- 2016 – The League launches, targeting ambitious professionals with exclusive, selective access.
- 2016 – Happn gains popularity for its unique approach of connecting users who have crossed paths in real life.
- 2017 – Facebook Dating is announced, integrating dating features directly into the Facebook ecosystem.
- 2017 – Feeld gains traction, catering to couples and singles exploring polyamory and alternative relationships.
- 2019 – Ship launches, allowing friends to help set each other up, making dating more of a social experience.
- 2020 – Pandemic Impact: Dating apps like Tinder, Bumble, and Hinge introduce virtual dating features to facilitate safe connections during lockdowns.
- 2020 – Facebook Dating launches in the U.S. with features like profile integration and “Secret Crush.”
- 2021 – Tinder adds “Hot Takes” and other interactive features, enhancing engagement and conversation starters.
- 2021 – Bumble and Tinder experiment with audio and video features, offering new ways for users to interact.
- 2022 – Snack gains popularity among Gen Z for its TikTok-style video approach to online dating.
- 2023 – Thursday launches, focusing on arranging real-life dates, but only being active one day of the week (Thursday).
The journey into online dating began with a technological leap driven by the advent of the internet. In 1995, we witnessed the launch of Match.com, a groundbreaking platform that ushered in a new era of matchmaking. Founded by Gary Kremen, Match.com quickly became a haven for individuals seeking romantic connections online.

Within just six months, it boasted over 100,000 users—a clear indication of the untapped potential in digital matchmaking. This early success set the stage for what would be a rapidly expanding market.
The essence of Match.com was not merely finding partners but fostering relationships through extensive user profiles and comprehensive searches. Users could upload photographs and fill out detailed questionnaires about their preferences, interests, and relationship goals. This personalization was revolutionary compared to traditional methods of dating, which often relied on chance encounters or matchmaking services without such depth.
As we moved through the late ’90s, Match.com’s commercial success demonstrated that online dating was more than just a passing fad. When Cendant Corporation acquired it in 1998 for $7 million, and later sold it to IAC for a staggering $50 million, it highlighted how valuable this emerging industry had become. By 1999, Match.com had cultivated a robust user base, paving the way for our current understanding of what dating apps could offer.
Just as we were getting comfortable with the concept of online dating, fresh platforms emerged in the early 2000s that disrupted the original format and reshaped our digital interactions.
1995-1999: The Birth of Modern Online Dating
With foundational platforms like Match.com capturing attention, we began to witness a shift towards community-based connectivity. Other trailblazers followed in its wake—namely eHarmony in 2000, which took compatibility matching to another level by using psychological assessments to pair users based on values and personality traits.

The introduction of Friendster in 2002 further transformed the landscape; it allowed users to create profiles connected through existing social networks. Although its innovative approach attracted many participants initially, technical issues like server crashes ultimately caused unrest among users. Consequently, this opened doors for other platforms seeking to refine user experiences.
It was during this budding period that OkCupid and Plenty of Fish emerged around 2003-2004, refining online dating’s focus on singles connecting directly without intermediary social ties. Through sophisticated algorithms and engaging questionnaires, OkCupid matched individuals not solely on physical attributes but using thoughtful queries that dug deeper into preferences.
With each progression from these pioneering sites came an understanding of what worked in digital matchmaking and what didn’t—laying essential groundwork for future innovations in the field as mobile technology started gaining traction in the coming years.
Integration of Smart Technology
The merging of smart technology into dating apps marked a pivotal moment that redefined user experience and enhanced the accuracy of matches. By 2020, it became increasingly common to see dating platforms incorporating artificial intelligence (AI) to refine their matching processes. This shift went beyond simple algorithms based on demographics or interests; apps began utilizing personal preferences and behaviors gathered from user interactions.
For example, algorithms analyze swiping habits, messaging styles, and overall engagement with potential matches to suggest profiles users are more likely to connect with. Studies show that 65% of users preferred apps featuring AI-driven functionalities. Our experiences helped notice patterns—what attracts us and what turns us away—which smart technologies help dissect and understand, leading towards improved dating outcomes.
As of 2023, over 50% of dating apps reported utilizing machine learning techniques to adapt and personalize user experiences continually. This means that every time we swipe left or right, our choices feed back into the app’s system, further refining its understanding of what works for us. It’s like having a personalized coach in dating who learns our preferences over time.
Alongside this adaptive approach, we have started seeing the introduction of augmented reality (AR) features, which offer users new ways to engage with one another virtually.
Augmented Reality in Dating Applications
The emergence of augmented reality in dating apps provides an immersive backdrop that changes how we interact online. With AR features, we can now have virtual dates that feel more interactive than ever before. Instead of just exchanging messages or images from our living rooms, we can invite someone into a shared virtual space where we can “meet” in a coffee shop setting or take a stroll through a park—right from our devices.

This innovative approach has gained traction among younger users who crave dynamic experiences that mimic real-life interactions. Research estimates that approximately 40% of dating apps incorporate some form of AR capabilities as part of their offerings. Not only does this cater to the desire for deeper connections, but it also fosters creativity and spontaneity in dating.
Having examined how smart technologies and augmented reality are shaping our interactions today, the next focus is on the revolutionary features that have transformed the landscape even further.
Game-Changing Features
The world of dating apps is a fascinating landscape marked by continuous innovation. The introduction of several game-changing features has played a pivotal role in this evolution. One of the most recognizable features is Tinder’s iconic swipe mechanism, which revolutionized how we approach potential partners. Instead of sifting through long profiles, users can swipe right to like or left to pass in an instant. This not only streamlined the decision-making process but also made searching for a match feel more like an engaging game. The adrenaline rush that comes with each swipe taps into our natural inclination for quick judgments, making the experience fun and less daunting.
It’s no wonder that many users are drawn in by this playful aspect. One user reflected on this point, stating, “Swiping right felt like a game, but it led me to my partner of three years.” Such stories remind us that beneath the surface-level engagement, there can be meaningful connections waiting to form.
However, it’s important to recognize the duality of such a feature. Critics argue that reducing individuals to mere images promotes a culture of superficiality. Yet, this simplification led to broader accessibility in dating—democratizing the matchmaking process and allowing more people to connect instantly based on mutual interest. The ease with which we can now interact has transformed dating from a more static experience into one that is dynamic and fluid.
Moving beyond swipes, Hinge entered the fray with an innovative approach by implementing the Gale-Shapley matching algorithm. This algorithm goes beyond just matching individuals based on aesthetics; instead, it prioritizes compatibility by selecting potential matches based on interests and values.
Our experience using Hinge showed us that thoughtful prompts encourage users to showcase their personalities rather than just presenting a curated image. By emphasizing conversation starters and deeper interests, Hinge cultivates an environment more conducive to genuine connections.
Similarly, Bumble’s female-first messaging policy has redefined interaction norms within dating apps. By allowing women to take the lead after a match is made, Bumble fosters respect and empowerment among its users. This shift not only creates a safer space for women but also encourages healthier conversations right from the start. As we navigate these digital realms, we find ourselves participating in a conversation about consent and control that resonates far beyond the app itself.
Each of these features contributes to an ongoing dialogue about how we create connections in our modern world. They shape both our personal experiences and broader societal expectations surrounding dating. As we adapt to these changing dynamics, questioning their effects becomes essential—not only on our individual lives but in society as a whole. Reflecting on these functionalities enables us to understand that while dating apps have changed how we meet people, they have also influenced what we expect from those interactions moving forward.
As we continue exploring this terrain shaped by technology, we’ll examine how these innovations ripple outwards, affecting cultural perceptions and social dynamics at large.
Social and Cultural Impacts
Dating apps have transformed how we connect with potential partners and how we perceive relationships in today’s society. The lines between casual and serious dating have blurred, giving rise to new relationship norms that reflect our fast-paced lives. People explore a variety of connections—some fleeting, others deeply meaningful.

One major impact we’ve witnessed is the redefinition of what constitutes a relationship. Once centred on traditional dating rituals, many now opt for more open-ended arrangements facilitated by these apps. Terms like “situationship” have emerged, highlighting relationships that may lack labels but brim with emotional connection. We navigate a complex world where clarity is often negotiated not through conversations but through swipes and messages.
As these changes unfold, they influence broader societal behaviours and attitudes.
Changing Communication Styles
Our communication styles are evolving too, thanks to the instant messaging capabilities of dating apps. Texting has largely replaced face-to-face conversation for initial interactions, which can be both a blessing and a curse. It allows us to express interest in someone without the pressure of an in-person meeting; however, it may contribute to misunderstandings or mixed signals. The impulse to craft the perfect message can heighten anxiety around dating for many individuals.
According to a 2023 study, over 45% of users reported feeling increased anxiety related to these online interactions, highlighting an emerging need for balance in communication practices.
“I find it simpler to talk behind a screen than face-to-face,” shared one user, exemplifying both the comfort and challenges of this digital dynamic.
Amidst these sweeping changes, we also encounter issues surrounding inclusivity and accessibility.
Inclusion and Accessibility
The rise of dating apps has opened doors for various demographics who previously faced barriers in traditional dating venues. LGBTQ+ individuals particularly benefit from platforms designed specifically for their communities. Apps like Grindr have provided safe spaces for people to connect, fostering environments where they can freely express themselves without fear of judgment or discrimination.
Yet, while we’ve made strides towards inclusivity, challenges remain. Not all platforms cater equally well to those with different abilities or backgrounds. The future will likely hinge on addressing these disparities within the app ecosystem.
As we consider what lies ahead in the evolution of dating culture, one notion stands out: adaptability is key.
Embracing Change
We must embrace these changes while being aware of the impact they have on our interpersonal relationships. As dating apps continue expanding their features—enhancing user experiences through video-first interaction or audio messaging—especially post-COVID—we’ll see further shifts in how we build connections.
To navigate this ever-changing landscape successfully, we can prioritize honest communication about our needs and preferences while respecting others’. Balancing modern technology with traditional values will be vital in ensuring that we foster genuine connections that stand the test of time.
With each swipe comes a unique story waiting to unfold—a testament that while technology shapes how we meet, it is ultimately we who dictate how deep those connections go.
The journey doesn’t stop here; as we look deeper into this topic, we will uncover the latest innovations shaping today’s dating space.
Emerging Trends in the Dating Application era
Technology is changing the landscape of how we meet and connect with potential partners. One of the most exciting trends we’re seeing is the rise of video-first apps. Platforms like Snack and Curtn have shifted the focus from mere text to video messages, allowing us to showcase our personalities more authentically. This not only fosters a greater sense of intimacy but also helps weed out mismatches based on superficial texts. When we can see someone’s facial expressions and hear their tone, it elevates our understanding and connection.
“In the age of instant messaging, seeing someone face-to-face—even through a screen—adds a layer of authenticity that text alone cannot convey.”
This leads us to another burgeoning trend: audio-first apps. Applications like String and Matter prioritize voice recordings over visual displays, encouraging us to engage on a deeper level that’s often overlooked. By focusing on voice, we can gauge emotion and sincerity in a way that images simply can’t capture. It’s as though we’re taking a step back to simpler forms of communication while still leveraging modern technology.
A survey indicated that apps incorporating audio features report higher user satisfaction rates, as many feel more comfortable revealing their personalities through conversation rather than photos or texts.
Additionally, there’s a strong push toward inclusivity across the dating app spectrum. Apps such as Salams and Muzmatch cater specifically to Muslim singles, while others like Glimmer serve individuals with disabilities, ensuring everyone feels represented and understood in the search for love. This wave of inclusivity highlights an essential need for tailored experiences, reminding us that romance should be accessible to all.
| Trend | Example Apps | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Video-First | Snack, Curtn | Emphasize video messages for personal connections |
| Audio-First | String, Matter | Focus on voice recordings over visual appearances |
| Inclusivity | Salams, Glimmer | Tailored for specific communities or needs |
Each of these trends signifies an evolution in how we interact with one another—seeking depth, authenticity, and personalization in our connections.
As we explore these innovations, it’s clear that promising developments are on the horizon regarding how we discover love online. The emphasis shifts from merely swiping right or left based on images toward more meaningful interactions rooted in actual voice and presence. These trends enrich our experiences while keeping us invested in the journey of finding companionship in this increasingly digital world.
Looking ahead, it is fascinating to consider how these trends will shape our interactions and experiences on dating platforms moving forward.
How have user behaviour and expectations shifted in relation to dating apps?
User behaviour and expectations in dating apps have shifted significantly towards seeking authenticity and meaningful connections rather than casual encounters. As of 2023, a survey revealed that 70% of users prioritize genuine conversations over superficial engagements, reflecting a growing desire for deeper relationships amidst an abundance of options. Moreover, features like video profiles and in-app icebreakers are increasingly popular, indicating that users expect more interactive and engaging experiences from these platforms. This trend underscores a collective move toward quality interactions as users navigate the complexities of modern dating life.







Leave a Comment